Running same old processes with new technologies – Cloud, AI, GenAI- is pure insanity. Rewriting them as Supply Chain Cloud Operating Models delivers new revenue streams, resilience and efficiencies.
When a word processor, e.g. MS Word, moves to the Cloud, it enables much more than word processing functionality, like collaboration, versioning etc., Similarly, when a supply chain functionality moves to the Cloud, several unconventional advantages are enabled, which are missed out if impactful technologies are simply infused into existing processes instead of rewriting them drawing on the advantages. This is applicable not just for Supply Chain but any functional area and any industry. Drawing from our team’s extensive experience of solving several Automotive manufacturers’ supply chain challenges, here are a few offerings with proven business value, not jargon laced confusions (control tower!):
- Parts Shortage – predict, prevent, and if unavoidable, manage the risk.
- Material Flow Orchestration – make sure each workstation has required components for the day’s production schedule, 100%.
- AI based workforce planning – not sexy but highest business value.
- Demand management with AI decisions to manage production constraints
- Inbound Inventory SKU forecast – apply Amazon scale SKU forecast strengths to tier-n components.
Connected, Cloud based approach to solving supply chain challenges opens several possibilities for extended, collaborative, correlated solutions besides solving the core operational challenges. It is fine to address supply chain issues in isolation – like inventory management at a location or for a plant. But the real, physical supply chains, unlike the ones represented in software systems, are never isolated and always have deep interrelatedness. Hence the true value of Cloud and various data capture technologies (IoT, Computer Vision etc) and data analytics technologies (simplified for the purpose of explanation – AI, GenAI, plain old OR, optimization etc) lies in solving for the this deep interrelatedness.
This post is a deep dive into Parts Shortage management (Reach out to SupplyChainWise for more details on this and other offerings). At a macro level, it is known that parts shortage impacts everything from planning and purchasing to customer experience, to even circular life or disposition, with an overlay of emission contribution through the parts’ life. So taking a comprehensive view of the impact across this span while solving for parts shortages needs an interrelated perspective of solution space. This same concept can be expanded to any other supply chain area, not just constrained to parts shortages.
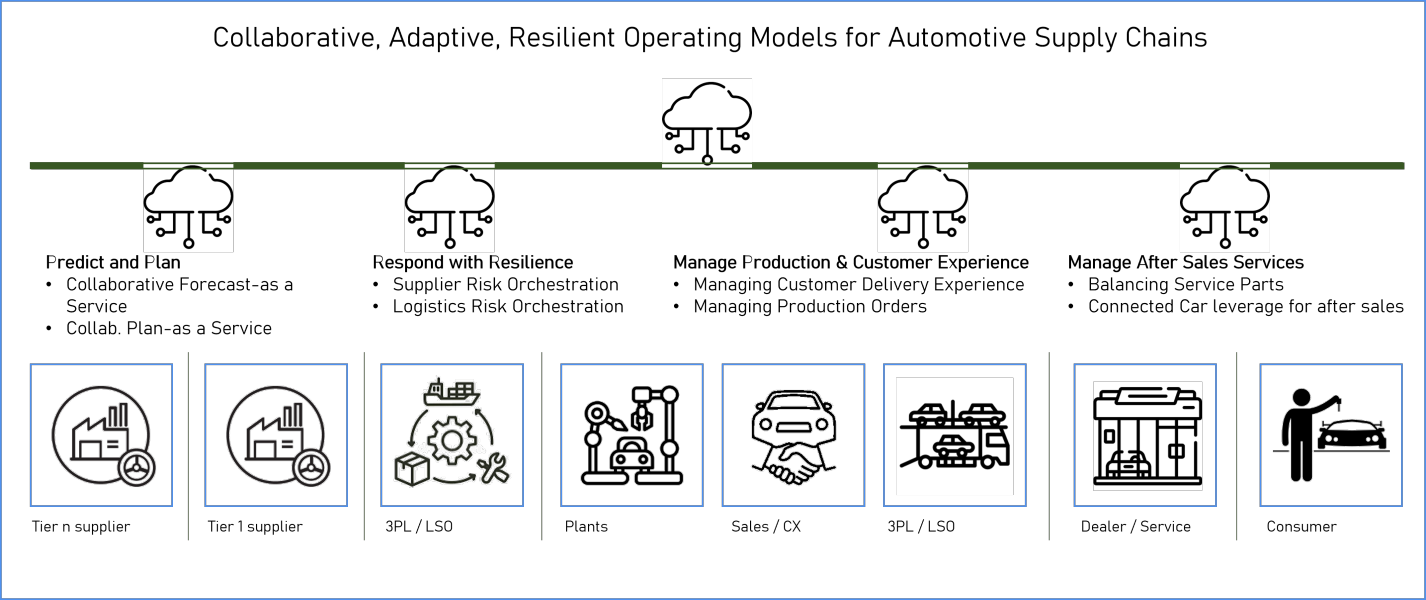
Parts shortage is a complex challenge with several aspects of causes and impacts. Gleaning from experiences across Automotive customers, instead of individual point solutions, here is a Cloud Operating Model that covers various aspects of this complex challenge with a cohesive set of solutions spanning the lifecycle of parts, not just purchasing or transportation or material flow or manufacturing etc. 1/Predict and Prevent 2/Respond and React with Resilience 3/ Manage Production and Customer Experience 4/ Manage After sales / market services.
While reading rest of the article, it is important to remember that the Cloud Operating Model inherently relates all the solutions components as one correlated ecosystem for use by internal users (internal to an auto manufacturer e.g,) and external users (suppliers, vendors etc.,), subject to permissions, access control and data security.
Predict and Prevent:
Structured, correlated data across supply chain participants with proven prediction models is the first place to start. Prediction of what is in your control, tier-N parts required, as accurately as possible using the best of technology is imperative.
Making use of highly granular predictions not used in Auto industry but perfected in other industries like Retail will go a long way in improving the forecast accuracy, at model-part-plant location-time granularity at individual part-supplier-week level.
But there is more to it. As an automotive manufacturer, the kind of impact your data and intelligence has on all tier-N suppliers is humongous. The Cloud operating model allows the auto manufacturer to share the strength of accurate forecasts can now be extended to and shared with the suppliers collaboratively in Forecast-as-a-Service model that benefits both the manufacturers and tier-N suppliers in an unprecedented way. Not just one time sharing but an online, shared, secure, selective visibility (a supplier can only see their relevance) into forecast will deliver production, logistics and delivery service level efficiencies.
This Cloud Operating Model also provides an incentive to share more visibility and transparency by tier-N suppliers with the OEM, a win-win outcome overall. And further incentivize tier-N suppliers to share any additional data when required using the same infrastructure (e.g., Emissions data).
The connected nature of this operating model helps in profiling supplier performance more accurately, in turn improving supplier service level predictions and more accurate production planning. Equally important is the predictions of supplier service levels accurately based on past delivery performance, quality performance and suppliers’ ability to accommodate changes.
In summary, solutions enabled by the Cloud operating model are
- Forecast:- Internal Forecast- Shared Forecast with tier -N (Cloud based Forecast-as-a-service model)
- Supplier profiling and service level prediction
- Collaborative Planning (Planning-as-a-Service)
- Virtual, Shared Inventory Planning
Respond and React with Resilience
Disruptions are bound to happen, several times. While no one can predict a disaster, one can be prepared with a systemic, data driven approach to take timely, informed decisions every time a disruption surfaces, with certain readiness, with some informed understanding of possible paths to recovery, beforehand.
Conventional approach of Plan and Pray – nice plans, great optimizations even with the best of AI/ML – does not provide a path to recovery when plans change. And plans change all the time as no intelligence can predict with great accuracy. Even What-If scenarios do not help much as there is a limit to the number of scenarios anyone can simulate. In the age of data, AI and Cloud, this need not be the case, there is no need to just plan and wait or simulate a few scenarios and wait!
The Cloud Operating Model follows a contextual approach leveraging data to keep the context prepared beforehand, so that when the realities change forcing the nice plans to fail, quickest path to recovery is systematically evaluated, in time, and informed decisions are recommended at the earliest to course-correct and recover, aiding rapid human decisions.
Unpredictability comes in all forms and shapes and plans change all the time – from large global events to parts getting delayed, not being available in expected quantities, unreliable supplier quality, shipping routes delays, MVOCC uncertainties etc., These challenges can be structured into 1/ Supply Risk (Supplier capacity, variation in available capacity, disruption in production, extraneous factors, Suppliers’ ability to react) 2/ Logistics Risk (Container availability, cost volatility, disruption in planned shipments, port congestion, container loading/unloading issues, port handoffs) and 3/Internal risks – (internal lack of prepared responsiveness i.e. data-driven mechanisms, lack of ability to respond to live, changing scenarios, lack of collaborative, quick response infrastructures)
In summary, solutions that enable resilience in the Cloud operating model are:
- Decision Inference and Recommendations- Decision alternatives – Suppliers- Decision alternatives – Carriers (Vessel-> Container -> Parts)- Simulation, Recommended Actions
- Impact Assessment- Affected Parts- Affected Freight Routes- Affected (Car/Vehicle) Models
- Composite, Live Supply Risk, covering- Supplier Capacity Risk (available capacity, variation, advance indicators, delay signals, quality events, lead time risk)- Logistics Risk (Vessel ETA, Vessel Disruption, Container Volume by route, Route Profiles, Port congestion, lead times, rates, Affected routes, parts, models, Alternative routes, suppliers).
Manage Production and Customer Experience
Even after all of the song and dance above, the reality forces Auto manufacturers to face parts shortage. At this stage, after having done everything one could, part shortages’ impact on customer experience (delivery dates, revenue impact, promotions or new model impact) and production (unplanned costs, schedules, model switches etc) need to be managed.
Instead of abandoning the decisions to the shop floor, a data and and ML driven solution space is enabled by the Cloud Operating Model, covering below aspects, providing informed, carefully evaluated decision alternative to the production shop floor in order to minimize customer impact while balancing revenue impact:
- Managing ProductionImpact Analysis and alternative actions– Impact analysis on models, plants, dealers, orders- Affected orders, revenue, marginsInference and Recommendations (Decision Recommendations, What Ifs, Manual override)- Reduced Vehicle Build- Vehicle Swap- Parts Expedite- Replaceable Components- Production Transitions (Leon- pls check)- Any other custom logicData driven decision evaluation to- Optimize revenues or other business targets (e.g. new model promotion)- Minimize losses- Protect / improve Service levels
Managing Customer Experience
While in the conventional business model of delivering vehicles through a dealer network, managing customer experience, from a manufacturer’s perspective, is far away from the customer, it need not be so. Especially if any manufacturer is exploring new business models like DTC – digital, online customization and purchase of a vehicle, to be delivered directly to the consumer. Even otherwise, in the dealer delivery model, respecting the promise of delivery date can be managed with intelligent, data driven approaches.
The Cloud Operating Model facilitates correlated context across manufacturing, marketing and sales and provides recommendations on which models, orders etc to prioritize while meeting the business objectives, with the below:
- Order Allocation Orchestration- Allocation Recommendation – new models, priority customers, promotions etc- Optimized for impact on Lead Time, revenue, Margin- Allocation preferences – partial / complete orders /simultaneous
- Customer Experience- Provide credible ETA promise to customers in the face of shortages- Updates in case of changes- Manage Lead Time- Adapt to changing buying habits
Managing Aftermarket Services:
Supplier constraints and part shortages on the production side will inevitably lead to shortages in servicing. Hence, using the evolving stronger data capture capabilities of connected cars to manage aftermarket impact of part shortages is important. This aspect of the Cloud Operating Model covers:
- Balancing parts with Aftermarket vs Production (prioritizing keeping cars on the road more than production – in case of recession etc.,)
- Manage parts risk / warranty risk
So What?
One may notice the stark difference in the focal points in the traditional vs Cloud Operating Model for supply chains above – designed for collaboration, data sharing, decision intelligence and resilience with secure, controlled data transparency at the core.
While these advantages themselves bring a sea change, the approach enables even more foundational changes to the business – like new revenue streams and new business models.
This topic will be expanded in later articles, but suffice it to say that several New Revenue Streams – e.g. Circularity – not at a cost but enabling revenue earning business with structured ReMan, RePlan, ReFurb etc models powered by the data and supplier connect from the above Cloud Operating Model and several New Business Models – e.g. business models using supply chain data for servicing, customer experience, resale, upgrades, cross-sell, etc., are facilitated by the Cloud Operating Model approach.
The conventional approach to solving supply chain challenges, even when ported to the Cloud or infused with the greatest of AI, GenAI, AGI etc., cannot achieve this.
Connect with SupplyChainWise for further details on this offering or specific case studies.